Harmonizing Just-in-Time Environments with Privileged Access Management
In the realm of cybersecurity, the fusion of Just-in-Time Environments (JIT) and Privileged Access Management (PAM) emerges as a dynamic solution, optimizing operational efficiency while fortifying security measures. This discourse delves into the symbiotic relationship between JIT environments and PAM, unraveling their advantages, deployment methodologies, and the consequential enhancements to organizational efficiency and security.

YouTube
Just in Time Permissions Explained #Delinea #PAM #CyberSecurity
Welcome to JITJea: Your Premier Source for Just In Time Privileged Access Management
What is Just In Time (JIT) Privileged Access Management?
In today’s complex cybersecurity landscape, the risk posed by standing privileged accounts—those with continuous, unchecked access to critical systems—has become a top concern.
Why JIT PAM is Essential for Modern Cybersecurity
- Reduce Attack Surface
- Improve Compliance
- Enhance Operational Efficiency
- Mitigate Risk of Credential Theft
How Delinea Powers Just In Time PAM
Key Features of Delinea’s JIT PAM Solution:
- Dynamic Access Provisioning
- Granular Access Controls
- Session Recording and Monitoring
- Risk-Based Access Policies
- Integration with Identity Providers
- Automated Credential Rotation
JITJea’s Expertise in Implementing JIT PAM with Delinea
- Assessment and Strategy
- Seamless Deployment
- Custom Policy Design
- Training and Support
Real-World Benefits of JIT PAM with Delinea
- Up to 90% reduction in attack surface related to privileged accounts
- Improved compliance audit readiness and reporting
- Faster detection and response to security incidents involving privileged access
- Enhanced operational agility and reduced manual overhead
Explore Our Resources
- Whitepapers
- Case Studies
- Webinars

This One Feature in PAM is one of the Coolest in the Whole Industry
- Minimized Attack Surface: JIT Access considerably lowers the attack surface by only allowing privileged access when absolutely required.
- JIT Access: guarantees that privileged access is momentary and context-specific, enhancing security.
- Operational Efficiency:
Monitoring and auditing access can take a lot of time for IT administrators. - Compliance and Auditability:
Strict control and documentation of access to sensitive systems are frequently necessary for regulatory compliance. - User Convenience: JIT Access maintains user convenience even in the face of strict security measures.
JIT Access is a prime example of how contemporary PAM solutions are changing to satisfy the competing needs of strong security and effectiveness.
4 Benefits of Just-In-Time (JIT) Privilege
Reduces Attack Surface
The Point:
Permanent privileged accounts increase the risk of
exploitation. JIT privilege eliminates standing access, ensuring
users have access only when needed.
Business Value:
- Minimizes exposure to credential-based attacks.
- Lowers the risk of lateral movement in cyberattacks.
- Reduces the number of privileged accounts attackers can target.
Enhances Security and Compliance
The Point:
Many compliance regulations require strict control over privileged access. JIT privilege ensures access is granted only when necessary and logged for auditing.
Business Value:
- Helps meet compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, NIST).
- Provides a detailed audit trail of privileged access activity.
How to Implement:
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for JIT access requests.
- Use session recording and logging to track all privileged activities.
How Compliance Views This:
- PCI DSS 7.1 & 8.1: Requires limiting privileged access and enforcing strong authentication.
- HIPAA Security Rule: Mandates strict controls over access to sensitive data.
Improves Operational Efficiency
The Point:
Traditional privileged access management requires manual intervention, slowing down workflows. JIT privilege automates access provisioning and revocation.
Business Value:
- Reduces IT overhead by eliminating the need for manual access approvals.
- Speeds up workflows by granting on-demand access without delays.
How to Implement:
- Integrate JIT access workflows into identity and access management (IAM) systems.
- Automate access provisioning and deprovisioning using privileged access management (PAM) solutions.
How Compliance Views This:
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): Requires strict access controls and automated enforcement.
- FISMA & NIST 800-171: Recommend automation to improve security and reduce manual errors.
Limits Privileged Credential Misuse
The Point:
JIT privilege eliminates persistent privileged credentials, reducing the likelihood of credential theft or misuse.
Business Value:
- Prevents misuse of standing admin privileges by insiders or attackers.
- Reduces the risk of compromised credentials being reused in future attacks.
How to Implement:
- Use one-time-use credentials or ephemeral access tokens for privileged actions.
- Implement privileged session management to monitor and control JIT access usage.
How Compliance Views This:
- ISO 27001 A.9.4.3: Requires organizations to enforce strict privileged access control.
- GDPR Article 32: Recommends limiting access to only necessary personnel.
Top 15 Mistakes Companies Make in Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is critical for securing sensitive accounts and reducing cyber risks. However, many companies make mistakes that leave them vulnerable to security breaches. Below are the top 15 most common mistakes organizations make when implementing PAM.
- Lack of a Comprehensive PAM Strategy
- Not Identifying All Privileged Accounts
- Overprovisioning Privileged Access
- Weak or Reused Passwords for Privileged Accounts
- Not Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Inadequate Session Monitoring and Auditing
- Failure to Regularly Rotate Privileged Credentials
- Ignoring Just-in-Time (JIT) Access
- Not Enforcing Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
- Neglecting Third-Party and Vendor Access Management
- Lack of Automated PAM Processes
- Poor Integration with Other Security Systems
- Failure to Conduct Regular Privileged Access Reviews
- Underestimating Insider Threats
- Not Preparing for PAM Implementation Challenges
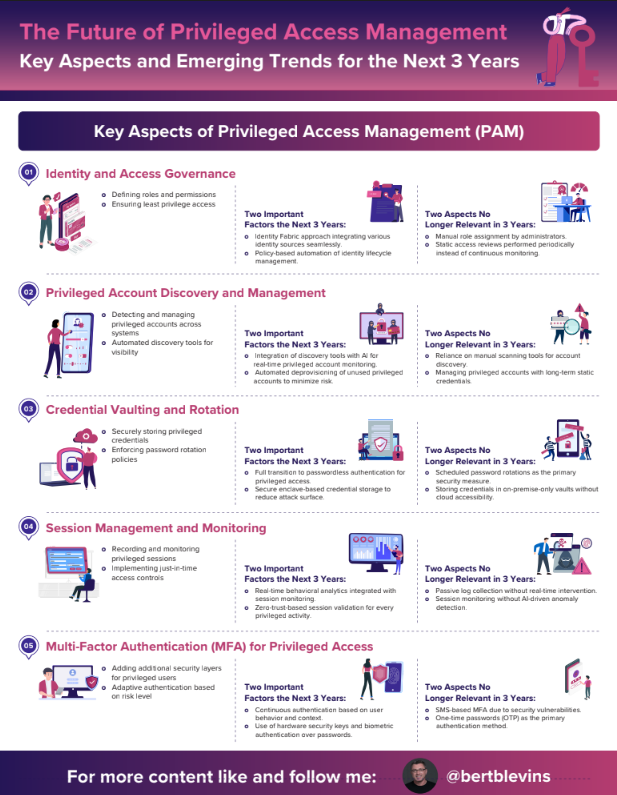
The Future of Privileged Access Management Key Aspects and Emerging Trends for the Next 3 Years
Key Aspects of Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Defining roles and permissions
- Ensuring least privilege access
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Identity Fabric approach integrating various identity sources seamlessly.
- Policy-based automation of identity lifecycle management.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Manual role assignment by administrators.
- Static access reviews performed periodically
instead of continuous monitoring.
- Detecting and managing privileged accounts across systems
- Automated discovery tools for visibility
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Integration of discovery tools with AI for real-time privileged account monitoring.
- Automated deprovisioning of unused privileged accounts to minimize risk.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Reliance on manual scanning tools for account discovery.
- Managing privileged accounts with long-term static credentials.
- Securely storing privileged credentials
- Enforcing password rotation policies
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Full transition to passwordless authentication for privileged access.
- Secure enclave-based credential storage to reduce attack surface.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Scheduled password rotations as the primary security measure.
- Storing credentials in on-premise-only vaults without cloud accessibility.
- Recording and monitoring privileged sessions
- Implementing just-in-time access controls
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Real-time behavioral analytics integrated with session monitoring.
- Zero-trust-based session validation for every privileged activity.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Passive log collection without real-time intervention.
- Session monitoring without AI-driven anomaly detection.
- Adding additional security layers for privileged users
- Adaptive authentication based on risk level
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Continuous authentication based on user behavior and context.
- Use of hardware security keys and biometric authentication over passwords.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- SMS-based MFA due to security vulnerabilities.
- One-time passwords (OTP) as the primary authentication method.
- Granting temporary privileged access as needed
- Reducing standing privileges and exposure
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- AI-driven risk-based JIT provisioning.
- Self-service JIT access with automated approval workflows.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Static, pre-assigned privileged access roles.
- Manual approval processes for privileged access requests.
- Using AI/ML for behavior-based risk assessment
- Detecting anomalies and potential insider threats
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Autonomous response to risky privileged behaviors.
- Deep learning-driven anomaly detection with contextual awareness.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Threshold-based anomaly detection models with static rules.
- Reactive security responses instead of proactive threat mitigation.
- Extending PAM capabilities to multi-cloud environments
- Managing non-human identities (NHIs) like service accounts and APIs
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- Centralized PAM for hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Automated identity governance for cloud workloads.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- PAM systems designed only for on-premise environments.
- Manual tracking of cloud service identities.
- Securing vendor and contractor access
- Implementing zero-trust principles for external users
Two Important Factors the Next 3 Years:
- AI-driven risk assessment for third-party access.
- Integration of continuous authentication for external users.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- VPN-based third-party access without real-time monitoring.
- Static access provisioning for contractors.
- Ensuring adherence to industry regulations
- Automating reporting for audits and compliance checks
An Important
Factor the Next 3 Years:
- AI-driven real-time compliance reporting.
Two Aspects No Longer Relevant in 3 Years:
- Periodic manual audits instead of continuous compliance monitoring.
- Siloed compliance reporting without centralized governance.
Unveiling the Essence of Just-in-Time Environments and Privileged Access Management:
- Just-in-Time Environments (JIT): JIT environments epitomize resource allocation precisely when necessitated, curbing excess and elevating efficiency levels. Expanding beyond traditional realms, JIT extends its influence to access provisioning and management within the cybersecurity domain.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): PAM serves as the vanguard in cybersecurity, curtailing and vigilantly monitoring privileged users' (e.g., administrators and IT personnel) access to critical systems and data repositories. Upholding the doctrine of least privilege, PAM systems ensure that users traverse solely through the corridors requisite for their designated roles and responsibilities.
- Mitigating Insider Threats: Insider threats loom large in environments permeated with privileged access. PAM solutions, through vigilant user activity monitoring and adherence to least privilege principles, serve as bulwarks against insider malfeasance, preempting the misuse or abuse of privileged credentials.
Augmenting Security in JIT Environments through PAM
- On-Demand Privileged Access: By aligning with JIT principles, access provisioning unfolds precisely when demanded, minimizing unauthorized entry and narrowing the attack vectors.
- Transient Privileges: Mirroring the JIT ethos of resource optimization, PAM platforms bestow temporary or time-limited rights, tethered to specific tasks or workflows. The exposure window dwindles as access automatically retracts upon task completion.
- Dynamic Access Controls: JIT environments necessitate adaptive access controls, capable of flexing in response to evolving requirements and circumstances. PAM systems empower enterprises to dynamically calibrate access privileges, factoring in variables such as user roles, contextual cues, and risk metrics, bolstered by granular access management tools and policy enforcement mechanisms.
- Auditing and Compliance: Through meticulous logging and reporting of privileged access activities, JIT environments fortified with PAM functionalities bolster auditability and regulatory compliance endeavors. Organizations can showcase adherence to security protocols and standards, thereby fortifying their regulatory posture.
Implementing JIT Environments with PAM
Articulate Access Policies: Enunciate access policies and delineate roles within the organizational hierarchy, aligning privileges with job functions and responsibilities.
Automate Access Provisioning: Harness automation tools and workflows to streamline access provisioning and deprovisioning, curtailing manual intervention and minimizing human fallibility.
Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance authentication resilience by integrating MFA protocols for privileged access, fortifying defenses against unauthorized intrusions.
Regular Access Reviews and Recertifications: Conduct periodic audits and recertifications of access privileges to ensure congruence with business imperatives and security requisites, promptly purging redundant privileges and roles.
Continuous Surveillance and Analysis: Instate robust monitoring and analysis frameworks to monitor privileged access activities, discern anomalies, and orchestrate real-time responses to security exigencies.

The amalgamation of Privileged Access Management with Just-in-Time paradigms furnishes a holistic blueprint for fortifying security postures while turbocharging productivity metrics. By imbuing access provisioning and control mechanisms with JIT principles, enterprises optimize resource utilization, mitigate risks, and bolster regulatory adherence. Through the deployment of PAM solutions, organizations fortify defenses against insider threats, instate least privilege protocols, and erect granular access constraints, thereby achieving the delicate equilibrium between cybersecurity resilience and operational efficacy in a dynamic.
Watching and Checking in Just-in-Time Environments with Privileged Access Management
In the quest to use resources wisely and safeguard important data and systems, it's crucial to keep a close eye on what's happening. This blog post explores why monitoring and auditing are so important in JIT environments with PAM, and shares some tips for doing it well.
Understanding Monitoring and Auditing in JIT Environments with PAM
Monitoring is all about keeping a constant watch on what users are doing, what events are happening in the system, and who’s accessing privileged information. It helps catch any unusual activity quickly and ensures that rules about who can access what are being followed.
Auditing is the process of carefully going through records of changes made to the system, security events, and who’s been accessing important information. It helps organizations see patterns of access and can be really useful for investigating incidents or looking for security problems.

Why Monitoring and Auditing Matter in JIT Environments with PAM
- Staying Legal: Monitoring and auditing help organizations follow laws like GDPR or HIPAA. By keeping good records and doing regular checks, they can show they’re following the rules and avoid getting into trouble.
- Keeping Safe: By spotting and dealing with any dodgy activity quickly, monitoring and auditing help lower the chances of something bad happening. It means organizations can fix problems fast and make it harder for anyone trying to break in.
- Dealing with Problems: If something does go wrong, monitoring and auditing can help figure out what happened and how bad it is. By looking at the records, organizations can work out who’s responsible and stop them doing it again.
- Doing Better: Monitoring and auditing don’t just help with security—they can also show where things could be done more efficiently. By looking at what’s happening, organizations can spot areas for improvement and make things work better.
Best Ways to Monitor and Audit in JIT Environments with PAM
- Get Alerts: Set up systems to tell you right away if anything suspicious is going on, so you can deal with it quickly.
- Keep Records Together: Put all the records about who’s accessing what in one place, so it’s easier to look through them and find out what’s happening.
- Check Regularly: Keep an eye on what’s happening regularly, so you can spot any problems before they get too big.
- Use Machines: Let computers help by automatically looking through records and picking out anything that looks wrong.
- Keep Learning: Keep finding ways to do monitoring and auditing better, so you can stay ahead of any new threats.
In JIT environments with PAM, monitoring and auditing are vital for staying safe, following the rules, and making things run smoothly. By keeping a close watch on what’s happening and checking regularly, organizations can keep themselves safe and be ready for anything that comes their way.
YouTube
OATH OTP MFA Explained: Easy Setup Guide for Stronger Security
About Me
Bert Blevins is a distinguished technology entrepreneur and educator who brings together extensive technical expertise with strategic business acumen and dedicated community leadership. He holds an MBA from the University of Nevada Las Vegas and a Bachelor’s degree in Advertising from Western Kentucky University, credentials that reflect his unique ability to bridge the gap between technical innovation and business strategy.
As a Certified Cyber Insurance Specialist, Mr. Blevins has established himself as an authority in information architecture, with particular emphasis on collaboration, security, and private blockchain technologies. His comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity frameworks and risk management strategies has made him a valuable advisor to organizations navigating the complex landscape of digital transformation. His academic contributions include serving as an Adjunct Professor at both Western Kentucky University and the University of Phoenix, where he demonstrates his commitment to educational excellence and knowledge sharing. Through his teaching, he has helped shape the next generation of technology professionals, emphasizing practical applications alongside theoretical foundations.

In his leadership capacity, Mr. Blevins served as President of the Houston SharePoint User Group, where he facilitated knowledge exchange among technology professionals and fostered a community of practice in enterprise collaboration solutions. He further extended his community impact through director positions with Rotary International Las Vegas and the American Heart Association’s Las Vegas Chapter, demonstrating his commitment to civic engagement and philanthropic leadership. His specialized knowledge in process optimization, data visualization, and information security has proven instrumental in helping organizations align their technological capabilities with business objectives, resulting in measurable improvements in operational efficiency and risk management.
Mr. Blevins is recognized for his innovative solutions to complex operational challenges, particularly in the realm of enterprise architecture and systems integration. His consulting practice focuses on workplace automation and digital transformation, guiding organizations in the implementation of cutting-edge technologies while maintaining robust security protocols. He has successfully led numerous large-scale digital transformation initiatives, helping organizations modernize their technology infrastructure while ensuring business continuity and regulatory compliance. His expertise extends to emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, where he helps organizations identify and implement practical applications that drive business value.

As a thought leader in the technology sector, Mr. Blevins regularly contributes to industry conferences and professional forums, sharing insights on topics ranging from cybersecurity best practices to the future of workplace automation. His approach combines strategic vision with practical implementation, helping organizations navigate the complexities of digital transformation while maintaining focus on their core business objectives. His work in information security has been particularly noteworthy, as he has helped numerous organizations develop and implement comprehensive security frameworks that address both technical and human factors.
Beyond his professional pursuits, Mr. Blevins is an accomplished endurance athlete who has participated in Ironman Triathlons and marathons, demonstrating the same dedication and disciplined approach that characterizes his professional work. He maintains an active interest in emerging technologies, including drone operations and virtual reality applications, reflecting his commitment to staying at the forefront of technological advancement. His personal interests in endurance sports and cutting-edge technology complement his professional expertise, illustrating his belief in continuous improvement and the pursuit of excellence in all endeavors.